(Photograph by iStock/Eoneren)
A permanent societal problem the world over is a “perspective deficit” in collective decision-making. Whether or not inside a single enterprise, at the local people stage, or the worldwide stage, some views aren’t (adequately) heard and will not obtain truthful and inclusive illustration throughout collective decision-making discussions and procedures. Most notably, future generations of people and facets of the pure atmosphere could also be deeply affected by present-day collective selections. But, they’re usually “unvoiced” as they can’t advocate for his or her pursuits.
Immediately, as we witness the fast integration of synthetic intelligence (AI) programs into the on a regular basis material of our societies, we acknowledge the potential in some AI programs to floor and/or amplify the views of those beforehand unvoiced stakeholders. Some lessons of AI programs, notably Generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT, Llama, Gemini), are able to performing because the proxy of the beforehand unheard by producing multi-modal outputs (audio, video, and textual content).
We refer to those outputs collectively right here as “AI Voice,” signifying that the beforehand unheard in decision-making eventualities achieve alternatives to precise their pursuits—in different phrases, voice—by way of the human-friendly outputs of those AI programs. AI Voice, nevertheless, can’t notice its promise with out first difficult how voice is given and withheld in our collective decision-making processes and the way the brand new know-how could and does unsettle the established order. There’s additionally an vital distinction between the “proper to voice” and the “proper to resolve” when contemplating the roles AI Voice could assume—starting from a passive facilitator to an lively collaborator. That is one extremely promising and possible chance for easy methods to leverage AI to create a extra equitable collective future, however to take action responsibly would require cautious technique and far additional dialog.
The Promise of AI Voice
On the subject of decision-making, social innovation practitioners and students have highlighted AI’s potential to amplify effectivity and improve creativity. On the identical time, many have rightly raised considerations
about equity, biases, and decreased human management. Along with these advantages and considerations, we contend that AI additionally presents a way to advertise social good by giving a voice to unheard stakeholders in collective decision-making processes.
Are you having fun with this text? Learn extra like this, plus SSIR’s full archive of content material, if you subscribe.
Traditionally, collective decision-making has been valued for its means to amalgamate various views, fostering selections which can be usually extra nuanced and complete than these formulated by people. This strategy has been championed by entities just like the United Nations, which promotes multi-stakeholder collective decision-making to develop extra adaptable, viable, and intensive options throughout the framework of the Sustainable Growth Objectives.
Nonetheless, conventional collective decision-making has limitations, usually sidelining stakeholders for causes of accessibility, discrimination, or comfort. Even when decision-making processes could also be as inclusive as doable, they might nonetheless omit vital views from those that can’t voice their views, similar to nature, animals, and future human generations. These later stakeholders play a important position in (the way forward for) our society, and their exclusion from collective decision-making may end up in options that lack depth and inclusivity. For instance, throughout the local weather debate, organizational and nationwide selections are sometimes pushed by short-term issues, overlooking the long-term impacts on nature and future human generations.
Inside this context, “AI Voice” emerges as an progressive resolution, proposing a option to harness AI for constructive social influence by amassing, processing, and presenting the views of silent stakeholders. Initially coined as a time period (in a paper co-authored by one in every of us and one other colleague, Andrew Sarta) to explain AI-driven suggestions specializing in the considerations of oft-overlooked enterprise stakeholders similar to clients, “AI Voice” could be interpreted extra expansively because the AI-generated human-friendly outputs, enabling AI programs to behave as proxies for these unheard stakeholders. As such, this time period doesn’t denote a selected services or products however as an alternative describes the output of sure AI programs, which could be utilized to present voice to unheard stakeholders.
For-profit organizations have already acknowledged the potential of utilizing AI programs to boost their decision-making processes, with a number of integrating this idea of AI Voice into their decision-making processes. As early as 2018, Einstein AI
participated in Salesforce’s weekly conferences, providing executives visible gross sales and consumer insights primarily based on buyer relationship administration information. Polish rum producer Dictador
and Finnish IT agency Tieto
have taken daring steps by designating AI entities in vital management capacities inside their organizations. Equally, a number of organizations are creating and deploying AI instruments
to facilitate group sense-making, deliberation, and finally decision-making.
In the meantime, nonprofit organizations and consortia have been comparatively sluggish in adopting AI functions into their management and wider decision-making processes. One notable exception is the case of WWF’s current initiative, “Way forward for Nature.” This London exhibition harnessed AI know-how to venture the doable futures of the UK’s atmosphere below varied eventualities of human intervention. Right here, AI Voice has been leveraged to articulate the views and predicaments of nature. It acted as a narrator, vividly illustrating the grim potential way forward for the pure atmosphere if the present tempo of degradation continues. It additionally depicted the promising transformations that may happen if pressing, corrective actions are taken. This AI-generated output has additionally been used as a dialogue instrument, permitting stakeholders, together with policymakers and activists, to discover and debate the potential penalties. On this capability, AI has shifted from merely a forecasting instrument to an lively agent aiding in creating environmentally sustainable methods. Nonetheless, there’s further potential for additional involvement of AI, similar to a speech system that might immediately contribute to those stakeholder discussions, giving a voice to the pure atmosphere within the dialogue.
This progressive use of AI exemplifies the broader capabilities of generative AI, which stands on the forefront of addressing the angle deficit in collective decision-making. In comparison with conventional AI, which focuses on categorization and evaluation, generative AI can generate seemingly new and artistic outputs.
In line with Demis Hassabis, co-founder and CEO of DeepMind Applied sciences, the output of generative AI could be categorized into three distinct varieties:
- Interpolated Output: Interpolated output refers back to the generative AI’s manufacturing of latest information factors or content material that matches throughout the class of already noticed information factors of its coaching dataset. This output kind is characterised by its similarity to the examples the AI was educated on. An instance could also be an AI educated to categorise and generate new cat photos primarily based on a coaching corpus of cat images.
- Extrapolated Output: Extrapolated output, alternatively, happens when the AI steps past the direct boundaries of its coaching information to generate content material. This output kind entails inferences or predictions about information factors exterior the speedy coaching set. Whereas nonetheless grounded within the underlying patterns realized throughout coaching, extrapolated outputs are extra speculative, pushing the boundaries of the AI’s realized context to create much less predictable and probably extra inventive content material. An instance could also be AlphaGo, the place, given all human information concerning the board recreation Go, it performs thousands and thousands of rounds in opposition to itself. Utilizing the perception gained throughout that course of, AlphaGo extrapolates new methods by no means seen earlier than in its coaching corpus (for instance, Transfer 37 in Recreation 2 – AlphaGo vs. Lee Sedol in Seoul, 2016).
- Invented Output: Invented output is the generative AI’s creation of completely new content material that isn’t immediately derived from its coaching dataset. This output kind showcases the AI’s means to innovate past realized patterns. An instance could also be an AI system educated in chess, creating the sport Go.
Most industrial generative AI functions primarily produce outputs that align with the primary two classes, interpolated and extrapolated. That is partly as a result of there are restricted mechanisms for successfully conveying the necessity for extremely inventive, ‘invented’ outputs to AI programs. Presently, AI struggles to course of and act upon extremely summary directions (e.g., designing a recreation that’s straightforward to be taught however presents complicated mastery and could be accomplished in an affordable timeframe). Because of this, these programs usually fail to generate outputs that mirror excessive ranges of creativity. This limitation underscores the significance of area consultants, similar to local weather advocates or biologists, who can perceive and interact with summary ideas. Their position in offering context and deciphering AI Voice is essential, bridging the hole between AI capabilities and the nuanced necessities of complicated duties.
The A number of Roles of AI Voice
Not all AI outputs—and by extension, AI Voice—play the identical position inside a collective decision-making course of. As an example, relying on the AI system’s stage of integration inside collective decision-making processes, an AI system could generate outputs that assist in organizing multi-stakeholder discussions or that provide beforehand unheard insights that contribute to complicated deliberations.
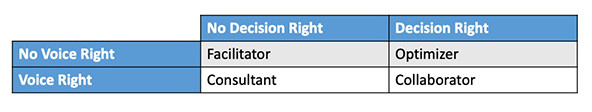
A helpful option to classify these potential roles for AI Voice is to make use of a field matrix with the 2 sorts of rights—rights of voice (voice rights) and rights to resolve (determination rights)—that people could grant within the particular course of. Voice rights grant AI the likelihood to supply insights and analyses on operational and strategic issues. In distinction, determination rights empower AI to partake within the conclusive phases of decision-making, together with casting a vote on initiatives. This differentiation results in 4 particular roles that AI Voice can assume inside collective decision-making processes: 1. Facilitator, 2. Advisor, 3. Optimizer and 4. Collaborator.
Facilitator Function: Within the Facilitator position, AI programs function with out voice or determination rights. Their perform is to not generate dialogue content material however to behave as organizational instruments. For instance, an AI system on this position may compile inputs from varied stakeholders earlier than a gathering. Subsequently, as a proxy for stakeholders who’re usually unheard, the AI Voice output may embrace an agenda that allocates particular time to deal with the considerations of those silent stakeholders. Moreover, AI Voice might be programmed to supervise the assembly, making certain adherence to cut-off dates and conserving discussions centered. This strategy helps assure that the decision-making course of stays inclusive and orderly.
Advisor: Within the position of a Advisor, AI programs are granted voice rights however not determination rights. This implies they analyze and interpret intensive information to advise decision-making processes however wouldn’t have the authority to make closing selections. For instance, think about an AI system tasked with evaluating the influence of city enlargement on native ecosystems. This technique would analyze environmental information and mannequin varied growth eventualities, presenting findings and suggestions to reduce ecological harm. Nonetheless, the ultimate decision-making authority rests with human stakeholders. On this capability, AI Voice offers stakeholders with in-depth, data-driven environmental analyses, thereby facilitating extra knowledgeable decision-making.
Optimizer: Within the position of an Optimizer, the AI system is provided with determination rights however doesn’t possess voice rights. Whereas the AI doesn’t recommend choices or affect outcomes with voiced opinions, it’s answerable for figuring out the simplest actions primarily based on objectives and constraints. The AI objectively analyzes the data supplied by stakeholders and employs a scientific strategy to find out the optimum distribution of assets or the simplest options to issues, all throughout the framework of established effectivity metrics and standards. For instance, an environmental company may deploy an AI system to allocate funding for conservation initiatives. The AI would assess every venture in opposition to important ecological efficiency metrics, similar to potential enhancements in species preservation or habitat high quality. The AI Voice would then distribute funds in a method that optimizes environmental outcomes, making certain selections are made objectively and free from subjective bias.
Collaborator: As a Collaborator, AI programs are granted each voice and determination rights, permitting them to take part totally within the decision-making course of akin to human members. On this state of affairs AI Voice contributes to discussions, proposes initiatives, and has voting rights on selections. It actively engages in dialogues, introduces proposals, and votes on resolutions. As an example, AI Voice built-in right into a wildlife conservation board is likely to be tasked with analyzing and presenting information on at-risk species. This AI, representing the pursuits of wildlife, would suggest methods to guard these species primarily based on its analyses. Moreover, it will partake within the voting course of, influencing the allocation of assets to make sure that the simplest methods for wildlife safety are prioritized and given a vote.
Whereas the Optimizer and Collaborator roles for AI Voice present promise, assigning decision-making rights to AI programs brings complicated moral issues to the forefront. It’s crucial to critically assess how and to what extent people ought to delegate decision-making obligations to AI. This entails inspecting shifts in ethical and authorized obligations accompanying AI’s use in decision-making capacities. Moreover, there’s a have to develop sturdy frameworks that can successfully govern AI’s conduct and be certain that its integration into decision-making respects moral requirements and authorized necessities.
Methods for a Accountable AI Voice
To make sure the accountable use of AI Voice and deal with its inherent challenges, we put forth three methods: stakeholder and area skilled involvement, transparency, and AI literacy. Nonetheless, these methods shouldn’t be seen as static suggestions however quite as encouragement for a steady dialog about accountable AI for good.
First, stakeholder and area skilled participation is essential in creating AI and using any AI Voice output, performing as a important line of protection in opposition to reinforcing present biases. By incorporating a variety of views and suggestions into the AI coaching course of, the system is educated on a extra complete set of various experiences and viewpoints. Such inclusivity is a deliberate technique to forestall skewed narratives and guarantee perspective authenticity. As an example, with out this breadth of enter, AI-generated content material could diverge from established moral or societal requirements, probably leading to confusion or hurt. Moreover, whereas AI Voice could mimic speech patterns, it doesn’t inherently grasp the complicated human experiences it seeks to emulate. Subsequently, area consultants are important in scrutinizing AI Voice outputs, providing recommendation on system refinements, and serving to to detect and rectify biases. Their experience ensures that AI evolves in a method that aligns with broader social values and contributes positively to decision-making processes. These stakeholders and area consultants also needs to be entrusted with the important process of figuring out the allocation of voice and determination rights to AI programs. This determination shapes the AI Voice’s stage of affect and duty in collective decision-making eventualities.
Second, transparency in AI deployment is crucial, particularly relating to its use case and the sources of its coaching information. Open disclosure of the place and the way AI is used clarifies its affect and the potential attain of its decision-making. Equally, clear documentation of the origins and composition of coaching information is prime to understanding the AI’s potential biases and limitations. This stage of transparency can pre-empt challenges associated to belief and accountability by permitting stakeholders to anticipate and perceive AI habits. As an example, transparency can stop the negligent use of AI in contexts for which it was not supposed or in conditions the place its selections might have unintended penalties. It additionally facilitates the identification of any gaps or overrepresentations within the coaching information, which, if left unaddressed, might result in skewed AI outputs. Moreover, transparency advantages AI programs by fostering person belief and facilitating extra knowledgeable and consensual integration into decision-making processes. It creates an atmosphere the place AI instruments could be extra readily scrutinized, refined, and, if vital, corrected by these with the related experience.
Third, enhancing AI and information literacy amongst customers is important. It ensures that people and teams utilizing AI for decision-making have the mandatory understanding to interact with this know-how successfully. Customers with information of AI’s information processing can discern its strengths and acknowledge when its performance is likely to be compromised, similar to when AI outputs seem inconsistent with anticipated norms. Being literate in AI allows customers to query the validity of the AI’s conclusions and to detect potential biases in its decision-making. This understanding is crucial for making certain that AI instruments are used appropriately and that their selections are built-in sensibly into general methods and operations. Moreover, understanding the information that powers AI fashions permits customers to advocate for information integrity and accuracy, contributing to the continued enchancment of AI programs.
AI can act as a considerable power for good when implementing the mandatory controls. Making certain information transparency and enhancing person understanding of AI are important steps towards accountable use. Participating varied stakeholders within the AI system design course of is equally important, notably when allocating voice and determination rights to AI programs. By combining these technical and participatory methods, we are able to leverage AI programs and AI Voice to deal with the “perspective deficit” in collective decision-making and create a extra equitable collective future the place future people and nature can higher thrive.
Help SSIR’s protection of cross-sector options to international challenges.
Assist us additional the attain of progressive concepts. Donate right now.
Learn extra tales by Konstantin Scheuermann & Angela Aristidou.
