Regardless of unprecedented progress in poverty discount over the previous few a long time, the size of the challenges we face at present remains to be daunting. Almost one billion folks lack electrical energy, over three billion lack clear water, and 750 million lack primary literacy expertise. On the similar time, many inventions to handle these points have already been invented: Technological innovation, corresponding to microclimate predictors for farmers, and cell cash, now permit us to succeed in the final mile like by no means earlier than, and there’s a wealthy panorama of social enterprises fixing the issues of poverty at native ranges all over the world.
As a result of only a few of those options attain the required scale, we have to explicitly confront the obstacles hindering profitable pilot initiatives and scale these improvements to sort out the complete magnitude of the issue.
Scaling Up Growth Influence attracts from a decade of expertise working with grassroots organizations. It acknowledges that scaling up is a dynamic strategy of transformation, the place greatest practices don’t essentially apply. It emphasizes that scaling requires placing the folks closest to the issue on the middle, understanding that they’ve the utmost information of their issues and thus are invaluable in co-creating long-lasting, scalable options. It examines scaling up from the lens of navigating advanced programs and highlights the position of steady studying, iteration, and adaptation. The ebook provides a very complete understanding of scaling up in its numerous dimensions, delving into scaling by means of for-profit enterprises, governments, and social enterprises, together with the essential position of funders.
In Chapter 5, “Scaling by means of Authorities,” we talk about the promise and pitfalls of scaling through the federal government. The excerpt under showcases two of three circumstances of scaling improvements by means of authorities featured within the chapter: the scaling of girls self-help teams in India and the scaling of an schooling mannequin in Brazil.—Isabel Guerrero, Siddhant Gokhale & Jossie Fahsbender
* * *
Scaling initiatives, applications, and insurance policies by means of authorities provides the best potential for growth affect. Governments sometimes have an enormous distribution community to succeed in the poor, unparalleled in measurement and attain, even relative to the biggest personal companies. Furthermore, governments command substantial budgets for social and financial companies, making it a robust participant at scale with the capability to duplicate confirmed improvements. For all these compelling causes, most social enterprises and different organizations in search of affect search to work with the federal government to affect change at scale.
Sadly, scaling by means of governments is especially difficult. Their slow-moving bureaucratic buildings restrict the environment friendly distribution of improvements to the final mile. Functionality constraints, corresponding to corruption, inadequate expertise, and lack of personnel, hamper the efficient implementation of companies. Complicated principal-agent issues additionally come up from the a number of targets of politicians, bureaucrats, and frontline service supply brokers; and the hurdles of implementation come up inside a hierarchical state system. One other roadblock to scaling improvements by means of governments outcomes from the shortage of coordination between completely different authorities departments leading to inertia and delays. Furthermore, authorities buildings of command and management, designed to keep away from failures, make it troublesome to innovate by means of an iterative strategy of trial and error. Lastly, political cycles prioritize short-term wins to attraction to voters, doubtlessly compromising the long-term funding in improvements wanted to resolve growth issues.
One answer to resolving these tensions lies in adapting greatest practices from for-profit enterprises to permit for innovation throughout the authorities system. As we noticed within the earlier chapter, classes from for-profits embrace: looking for a Minimal Viable Intervention that’s easy, cost-effective, and simple to implement throughout completely different contexts; designing applications with the person on the middle; tapping into the information of the federal government worker on the final mile who is commonly neglected regardless of being closest to the supply of the issue; iterating to discover a answer earlier than scaling; and utilizing agile strategies for implementation. Studying from for-profit enterprises additionally consists of emphasis on accountability, high quality of service, effectivity, pace, and a much less hierarchical construction than conventional bureaucratic programs.
On this chapter, we talk about how scaling up applications or initiatives inside governments supply completely different challenges, particularly relative to the personal sector. We then supply examples of two completely different pathways to scale, one taking improvements developed within the personal sector or social enterprises to the federal government for scale, and the opposite innovating throughout the authorities itself. Governments additionally play an important position in policymaking and influencing the regulatory setting. We reserve the dialogue of the federal government’s position in managing the regulatory environments, particularly for social enterprises, for Chapter 9.
Two Pathways to Scale By means of Authorities
There are two pathways to scale by means of authorities. The primary pathway entails the federal government leveraging its scale and distribution to duplicate improvements initially developed by civil society or within the personal sector. It is a helpful pathway given the issue of making areas for innovation in authorities, particularly when failure is politically expensive. As an instance this, we give attention to girls’s self-help teams in India, which started as an innovation to enhance empowerment, developed by civil society organizations, and ultimately grew to become a part of India’s most vital poverty alleviation program at present.
The second pathway is to innovate throughout the authorities; as an example this pathway we’ll talk about two examples. The primary is a profitable schooling reform in Sobral, Brazil, which reveals the facility of experimentation, iteration, and studying to realize higher studying outcomes. Sobral’s schooling mannequin is at the moment being examined on the federal degree in Brazil and has impressed schooling reforms in Pakistan and Kenya. The second instance is Progresa/Oportunidades, a conditional money switch program in Mexico, which reveals a extra conventional strategy to authorities innovation, with large-scale pilots, rigorous affect evaluations, and a gradual strategy of constructing political assist and financial house. Oportunidades scaled to five million households in Mexico and survived 4 six-year presidential phrases. It impressed conditional money transfers throughout Latin America and the growing world.
Taking Exterior Improvements to Authorities
The Nationwide Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) in India: A 40-year Story
NRLM is a flagship poverty discount program of the Ministry of Rural Growth (MoRD) in India. This system organizes poor girls into federations of self-help teams (SHGs) to extend their earnings and improve financial empowerment. The roots of NRLM will be traced again to improvements that grassroots and civil society organizations developed over many a long time that have been ultimately tailored and replicated by the federal government to succeed in over 80 million girls.
The seeds of NRLM emerged from a wave of social mobilizations within the late Nineteen Sixties and early Seventies, that began girls’s community-based organizations with the formation of the Mysore Resettlement and Growth Company (MYRADA) and the Self-Employed Ladies’s Affiliation (SEWA). By the Nineteen Eighties, PRADAN, together with MYRADA, was working and experimenting with the primary self-help teams that have been remarkably related in formation to the self-help teams at present.1,2 These efforts have been first supported by the federal government by means of a pilot program that linked these teams to banks by means of the Nationwide Financial institution for Agriculture and Rural Growth (NABARD), thereby offering the early scaffolding and basis for scale.
Within the late Nineteen Nineties, a number of initiatives to discover scaling this innovation emerged. Considered one of them was a UNDP 3-year pilot for SHGs in South Asia.3 The challenge centered on BRAC in Bangladesh, Aga Khan Rural Help Program (AKRSP) in Pakistan, and Amul (a dairy cooperative) in India. The Pakistan part was designed for village growth in distant areas the place the state had by no means reached. In Bangladesh and in India the initiatives regarded on the learnings from applications that had scaled. The pilots in India focused small teams and supplied substantial financing.
Additionally, within the later Nineteen Nineties the rising prominence of SHGs caught the eye of the Ministry of Rural Growth (MoRD) which had launched the Swarnajayanthi Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY) that was geared toward enhancing self-employment and skill-development. By the early 2000s, the SHG linkage with banks, layered with talent growth and coaching, expanded in state governments. This growth was partially as a result of proof of idea demonstrated by the UNDP pilot that paved the trail for different states.
Within the decade that adopted, there was in depth experimentation with completely different fashions and adaptation to completely different realities as SHGs grew to become central to state rural growth applications. Andhra Pradesh was an early success. A number of states adopted the Andhra Pradesh mannequin and, at this stage, the World Financial institution4 performed an vital position in selling SHGs on the state degree, helping in financing and operationalizing the innovation. The Kerala state livelihood mission, constructed from inside their civil society and village authorities motion, embraced SHGs in a unique strategy. Bihar, a state that was thought of incapable and susceptible with widespread poverty and rampant corruption, reworked the mannequin to reply to their wants. This new mannequin began with the federal government retiring high-cost debt and growing non-farm livelihoods; it has develop into a massively profitable program constructing on contextualized information throughout the state.
Based mostly on the success of a number of state livelihood applications, NRLM was established in June 2010 in a radical departure from earlier rural growth applications. NRLM was designed to develop into one of many key pillars of rural poverty discount efforts in India, mobilizing all rural, poor households into SHGs and SHG federations offering entry to credit score and different technical and advertising companies. With World Financial institution assist, MoRD created knowledgeable service supply structure primarily based on the outcomes of state-level rural livelihood initiatives. The nationwide strategy was additionally designed by means of a strategy of experimentation and adaptation, beginning with ten high-poverty states to create a mannequin for NRLM for future growth.
At this time, though a lot work stays to actually attain recognition, dignity, and independence for rural girls, the Nationwide Rural Livelihoods Mission reaches roughly 83 million girls. It’s the largest livelihood program on the earth, and it began from grassroots improvements that established the ‘proof of idea’ over a interval of thirty years earlier than the federal government was able to scale it up on the state degree first after which on the nationwide degree.
This primary pathway to scale, whereby innovation is first developed outdoors the federal government, takes appreciable experimentation and adaptation earlier than it is able to go to a nationwide degree. As we are able to see in Determine 5.1, girls’s collectives and SHGs have been examined for 20 years earlier than there was proof of idea that organizing girls helped change behaviors and activate company. The primary manifestation of this variation was within the means of SHGs to avoid wasting, faucet into finance, and really feel represented by village organizations and federations that would join them to authorities applications.
Determine 5.1: The Phases of Scaling Up Self-Assist Teams by means of Authorities
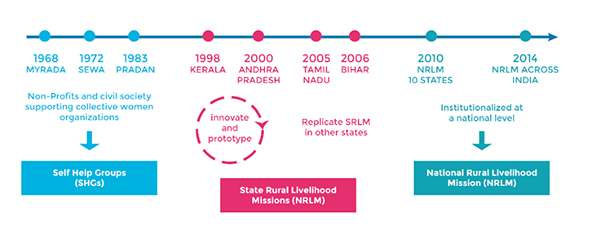
Additionally it is clear from this illustration that the intermediation position is a crucial prerequisite for fulfillment in scaling by means of authorities. A number of organizations, corresponding to UNDP, performed that position for SHGs within the transition to scale by means of states. As soon as the UNDP challenge confirmed proof of idea, it was essential to have a couple of champions on the state degree with the liberty to experiment and adapt to their very own realities. Given the dimensions and variety of India, it’s not stunning that the path to scale at a nationwide degree might solely be possible after many states had develop into champions of SHGs. Given India’s measurement and variety, constructing belief and possession state by state is the one approach for applications to scale whereas sustaining sustainability.
Innovating and Scaling By means of Authorities
The Strategic Triangle
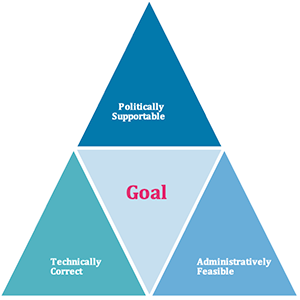
Working throughout the authorities introduces new layers of complexity that aren’t current in for-profit enterprises. A scalable coverage, program, or intervention in a authorities context should meet the three standards that are summarized in Determine 5.2: technical correctness (effectiveness), administrative feasibility (implementability), and political supportability (essential buy-in). Many authorities initiatives, applications, and insurance policies fail as a result of they’re missing in a number of elements of this trinity.
Technical correctness assesses whether or not an intervention works successfully in numerous difficult circumstances, corresponding to low-capacity settings, distant areas, and numerous areas throughout the nation. It’s typically measured by affect evaluations. Administrative feasibility evaluates whether or not the intervention will be applied by the state paperwork, contemplating the funds/value constraints, capability limitations (together with property, expertise, and personnel), and current rules. Lastly, political supportability ensures the required buy-in amongst key political actors and ensures the sustainability of the intervention for long-term affect. Too typically, we see interventions that work and are even implementable however don’t final due to adjustments within the political setting.
Determine 5.2: The Strategic Triangle of Efficient Coverage Design
Navigating the authorizing setting, particularly throughout the authorities, will be difficult attributable to their fragmented and hierarchical natures, with a number of brokers performing below numerous incentives. As we noticed in Chapter 3 on programs, inside a fancy multi-stakeholder system we’ll discover many breakage or leverage factors. Participating related stakeholders from the design part helps determine interventions which might be viable, authentic, and related for the precise context.
The strategic triangle provides a helpful framework to evaluate the scalability of interventions in authorities but in addition describes the distinctive challenges of working with governments. We now flip to the pathways to create scalable interventions inside authorities with all three components of the strategic triangle.
The Case of Sobral
The schooling reform in Sobral (Brazil) is an instance of innovation throughout the authorities that has led to profitable long-term outcomes.5,6,7 Regardless of being in Ceará, one of many poorest states within the nation, Sobral now has the very best main and decrease secondary schooling in Brazil. Between 2005 to 2017, Sobral went from rating 1,366 to being the very best performer within the nationwide index of high quality of schooling. This modification was potential because of a sustained schooling reform incorporating steady studying and iteration whereas sustaining political assist.
The spectacular shift in studying outcomes is the results of a course of that has required greater than 20 years of effort. A diagnostic evaluation in 2000 confirmed that solely 62% of second-grade youngsters might learn.8 Municipal leaders realized that every one the efforts to extend pupil enrollment weren’t main to higher studying outcomes and determined to set a transparent purpose for all college students to be literate by the tip of second grade. The literacy drawback had a number of root causes: the varsity community was fragmented with too many small colleges; youngsters began literacy schooling too late; there was an absence of assist for lecturers and pedagogical supplies weren’t efficient; there have been no incentives for lecturers and administrators to enhance; and college administration wanted to be strengthened.9
Municipal leaders began by specializing in two short-term actions. To sort out the late begin to literacy schooling, they handed a legislation to start out main schooling at age six as an alternative of seven. This modification was politically supportable and administratively possible as a result of it might be addressed by means of a municipal legislation. Mother and father and lecturers have been open to the change and the municipality had the financial and human sources to implement it. To unravel the issue of getting too many small rural colleges, the following step was to consolidate the variety of municipal colleges from 96 small colleges to 38 bigger colleges with higher circumstances. This modification had political assist from the federal government that had acknowledged the issue of multi-grade school rooms. Nevertheless, mother and father didn’t welcome the change due to transportation challenges. The municipality created sufficient assist to start the reform by offering transportation for college students and assembly with the neighborhood to acquire mother and father’ assist.
Between 2001 and 2004, the municipality applied reforms on 4 strategic ranges: secretariat-level administration, faculty administration, pedagogy, {and professional} incentives. On the first degree, they launched exterior assessments and common visits from the superintendent group, with indicators to watch every faculty. On faculty administration, they launched technical choice standards for the principals, gave extra monetary autonomy to the faculties, and put in pedagogical coordinators within the colleges. In pedagogy, they developed detailed literacy instructing supplies, supplied month-to-month coaching to lecturers, and set month-to-month and weekly studying targets. Lastly, they launched the “Escola Alfabetizadora Prize” that gave financial incentives to lecturers, coordinators, and principals primarily based on studying targets.
The usage of knowledge and common suggestions mechanisms have been key to evaluate the technical correctness of the proposed interventions and to take care of political assist from all stakeholders. The common suggestions mechanisms allowed them to mirror on the precise actions involving all native actors by means of weekly conferences between principals and pedagogical coordinators, periodic visits from the coordinators, weekly conferences between faculty principals, and bi-monthly visits from the varsity superintendent. Throughout these conferences, they mentioned challenges and classes discovered from implementing these new insurance policies within the classroom. This was complemented by exterior assessments of scholars’ efficiency relative to the targets. By means of this course of, the municipality was in a position to present well timed knowledge to maintain assist from mother and father and colleges and maintain increasing assist inside the federal government.
Sobral is a profitable instance of the right way to innovate throughout the authorities. It reveals the extent of complexity and the size of time required when scaling by means of authorities. Different states and nations have been impressed to duplicate the success of Sobral. This system “Educar pra Valer”10 is taking the expertise from Sobral to different municipalities in Brazil, ranging from 5 in 2018 and increasing to 23 municipalities in 2019, throughout 12 states. Furthermore, the present Minister of Schooling is scaling up Sobral’s reform to the Federal Stage by means of the “Criança Alfabetizada” program.

